¿Son las apps una chapuza temporal?

Sé que esto es tirar piedras contra mi propio tejado ya que yo me gano la vida gracias sobre todo a aplicaciones Android, pero no puedo dejar de pensar que el fenómeno de las apps móviles me recuerda a lo que pasaba hace 10 años en los ordenadores de escritorio, cuando teníamos que descargar una aplicación para Windows, otra para Mac… substitúyase esto por Android, iOS y Windows Phone… sí señor, aplicaciones de escritorio, ¿a que suena rancio?
¿Y por qué Google, que se supone tiene a los mayores expertos en web del mundo apoyó Android cuando tenía un sistema operativo basado en web como ChromeOS? Para mi la respuesta es que la web móvil no estaba preparada y los navegadores móviles no conseguían la suficiente potencia para simular una experiencia nativa. Y es que a día de hoy Android, mejor dicho, la máquina virtual java (JVM) Dalvik, sigue consiguiendo mejor rendimiento que los motores HTML5 móviles (que yo considero también máquinas virtuales), y aunque éstos mejoran día a día, debido a las limitaciones de Javascript (JS) es muy difícil que se aproximen al rendimiento de una JVM.
También podría ser que la mejora de las CPUs móviles haga que no importe el menor rendimiento de las aplicaciones web.
Y está el moviento extraño de Google con Dart. JS es malo, pero… ¿crearte un lenguaje nuevo tú sólo? ¿sin contar con ninguno de los otros actores? Google ya parece Microsoft en sus mejores tiempos ¿recordáis del malogrado VBScript para HTML? Puede ser que la gente de Google sí crea que el futuro está en la web, pero no con JavaScript.
Por otra parte estoy viendo decepcionado como Google se resiste a integrar la Chrome Webstore en Google Play, privándonos de poder publicar aplicaciones HTML5 para Android directamente (sin recurrir a chapuzas como PhoneGAP), también veo cómo Google y Apple siguen proporcionando WebViews del paleolítico capando APIs tan esenciales como WebGL ¿Y por qué? ¿Acaso abrir las puertas a las aplicaciones HTML5 es matar la gallina de los huevos de oro de las apps? Alguien en Cuppertino y en Mountain View debe pensar que sí.
Y aquí entra el, de momento fracasado, FirefoxOS. La gente de Mozilla sí ve claro el futuro en la web. FirefoxOS no es más que un Android al que le cambian la JVM Dalvik por el motor HTML5 Gecko. Tampoco me parece que FirefoxOS tenga mucho sentido ya que es más fácil instalar Firefox en cualquier dispositivo Android y se tiene igual acceso a todas las aplicaciones del Firefox Marketplace. Sin embargo, Firefox con su Marketplace es, en mi opinión, la mejor forma de distribuir y ejecutar aplicaciones HTML5 en un móvil. Pero Firefox está disponible sólo en Android, las políticas de Apple impiden explícitamente usar motores web que no sean el suyo, de nuevo… ¿miedo a las aplicaciones HTML5?
En los últimos 10 años hemos visto como las aplicaciones web substituían a muchas de las aplicaciones que usábamos cada día en nuestros equipos de escritorio, ¿sucederá esto con las apps móviles? Pues no lo sé, dejemos esto de adivinar el futuro para los programas nocturnos de las televisiones.

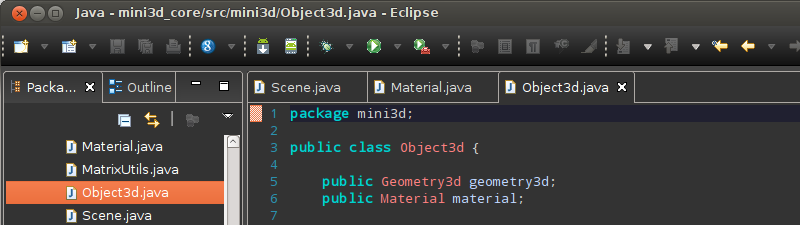 Getting back to the old days where I used Emacs to code (ok, more than ten years ago), now I’m using a dark theme in Eclipse. Dark themes are less eye-stressing and now are becoming popular with editors like IntelliJ, Sublime Text and the last Visual Studio. And that’s why more people is learning to programming even to his difficulty, although there are strategies that people can use to improve their learning, so you can use all the power of your mind to learn, you could visit
Getting back to the old days where I used Emacs to code (ok, more than ten years ago), now I’m using a dark theme in Eclipse. Dark themes are less eye-stressing and now are becoming popular with editors like IntelliJ, Sublime Text and the last Visual Studio. And that’s why more people is learning to programming even to his difficulty, although there are strategies that people can use to improve their learning, so you can use all the power of your mind to learn, you could visit 
 GWT
GWT CoffeeScript
CoffeeScript Haxe
Haxe Dart
Dart Ok, I’m supossed to be an Android developer, but i’m going back to HTML+JS for some projects, and I found that HTML5 has really powerful new APIS, these are my favourite:
Ok, I’m supossed to be an Android developer, but i’m going back to HTML+JS for some projects, and I found that HTML5 has really powerful new APIS, these are my favourite: